KABOOM! Why Do Cancer Cells Use Aerobic Glycolysis
Therefore they rely heavily on the glucose and rapidly convert it to pyruvate via glycolysis. Warburg suggested that cancer cells use aerobic glycolysis because their OXPHOS apparatus is injured and that this damage is a necessary step on the progression to a metastatic phenotype 3.
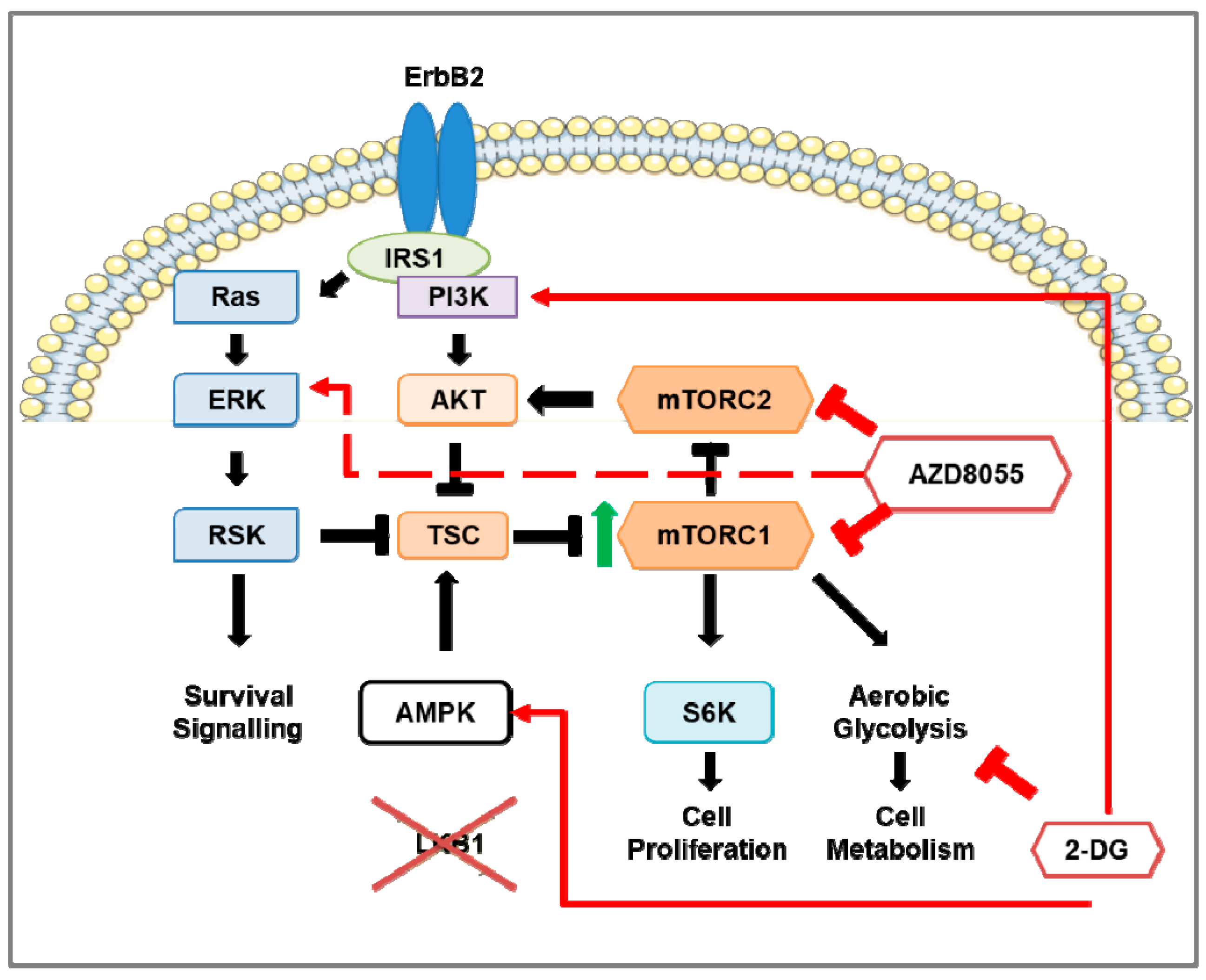
Cancers Free Full Text Targeting Mtor And Glycolysis In Her2 Positive Breast Cancer Html
In contrast cancer cells rely mainly on the first part of the energy production process dependant on glucose sugar this is an anaerobic process.
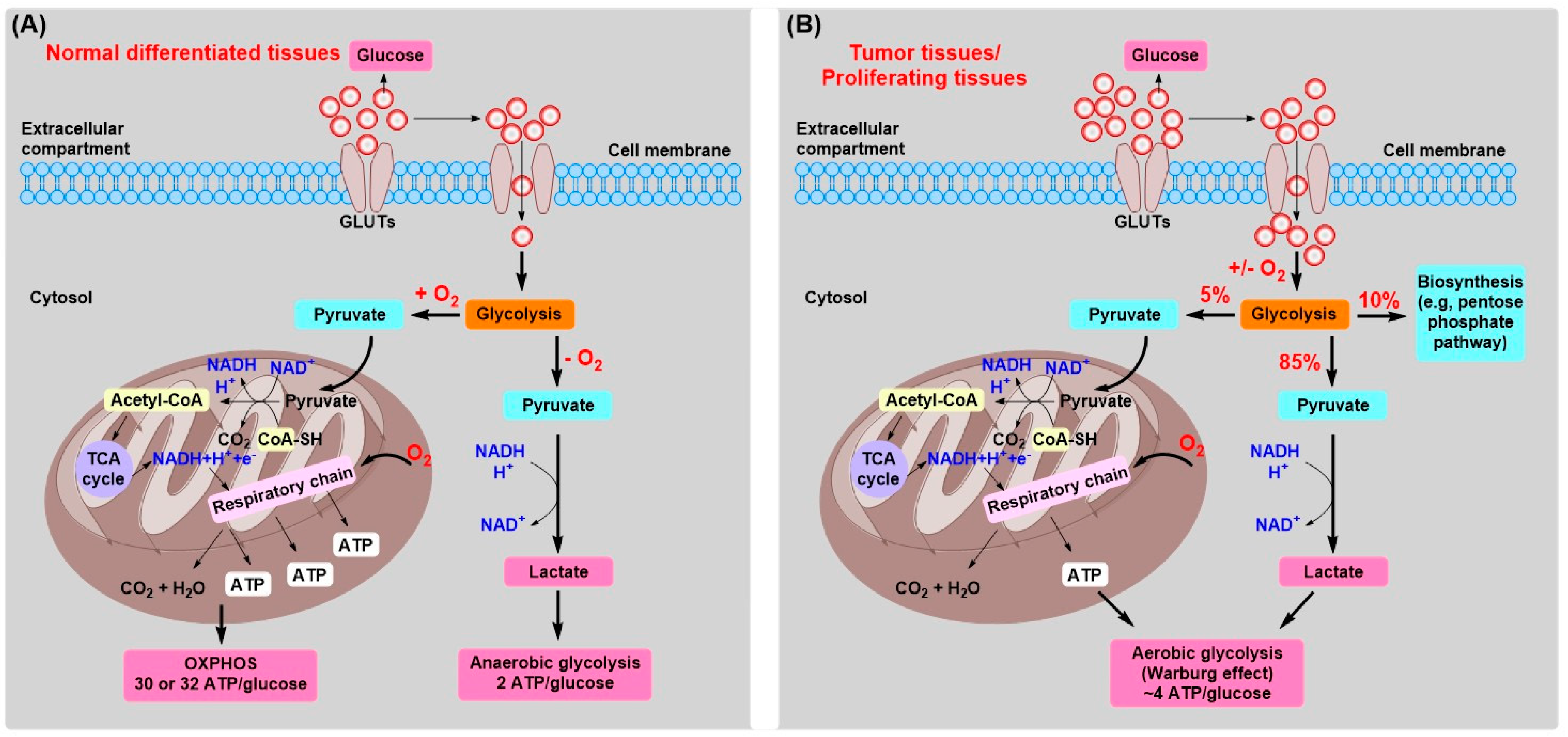
Why do cancer cells use aerobic glycolysis. Many studyies with different hypothesis have emerged trying to explain this this property in cancer cells. Constitutive aerobic glycolysisthe Warburg effectis a hallmark of cancer cells that is commonly caused by mutations in oncogenes and tumor-suppressor genes Blaydes and Birst wrote in. These observations indicate that altered metabo-lism of glucose by tumours is more than a simple adaptation to HYPOXIAWe suggest that the near-universal observation of aerobic glycolysis in.
Cancer cells exhibit aerobic glycolysis. Why do cancer cells use aerobic glycolysis to produce energy. Yeast cells do not switch to anaerobic respiration no can do they switch to fermentation.
Cancer cells turn on aerobic glycolysis so they could grow more rapidly and compete for energy. This communication analyzes why cancer cells switch from OXPHOS to glycolysis in the presence of adequate oxygen levels and how these cells manage to avoid the inhibition of glycolysis induced by oxygen. This means that cancer cells derive most of their energy from glycolysis that is glucose is converted to lactate for energy followed by lactate fermentation even when oxygen is available.
Yes some cancer cell lines use aerobic glycolysis always and some do have defective OXPHOS apparatus. Cancer cells actively produce more glucose transporters on their cell surface membranes so more glucose is brought inside the cellOnce inside the cell the glucose is broken down by aerobic glycolysis into lactic acid in order to speedily produce ATP and metabolic precursors through various metabolic pathways. To meet their energy and material needs cancer cells steal glucose from their microenvironment and produce lactic acid.
This produces far less. Thus a reasonable hypothesis on the reason that cancer employs aerobic glycolysis should account for this inherent difference in kinetics. Cancer is defined by uncontrollable cell growth and division so cancer cells need the building blocks and energy to make new cells much faster than healthy cells do.
However it has been known for many years that cancer cells and non-malignant proliferating cells can activate glycolysis in the presence of adequate oxygen levels aerobic glycolysis. Normal adult cells use a small energy plant located inside them to produce most of their energy needs from oxygen this is an aerobic process. Why do cancer cells prefer anaerobic glycolysis.
Since proliferation of cancer tissues is faster than normal tissues it not only needs energy but also needs metabolic intermediates for the biosynthesis of. Therefore they rely heavily on the glucose and rapidly convert it to pyruvate via glycolysis. Enhanced aerobic glycolysis do not mean aerobic oxidation and the tricarboxylic acid TCA cycle has been 100 blocked.
Some researchers explain that this type of metabolism is used because the tumor environment lacks sufficient oxygen to support the uncontrolled proliferation and high-metabolism rate of malignant cells. A considerable amount of knowledge has been produced during the last five years on the bioenergetics of cancer cells leading to a better understanding of the regulation of energy metabolism during oncogenesis or in adverse conditions of energy substrate intermittent deprivation. Cancer is defined by uncontrollable cell growth and division so cancer cells need the building blocks and energy to make new cells much faster than healthy cells do.
The Warburg effect present that cancer cells enhance aerobic glycolysis to generate energy and supply intermediate for macromolecule biosynthetic including ribose-5-phosphate glycine for nucleotide or glycerol for lipid. Cancer cells prefer to use aerobic glycolysis for ATP production while still retaining the function of OXPHOS for the following reasons. This is termed the Warburg effect.
Several strategies and drugs that may interfere with the glycolytic metabolism of cancer cells. Why do cancers have high aerobic glycolysis. I Glycolysis is more suitable for cancer growth.
This means that cancer cells derive most of their energy from glycolysis that is glucose is converted to lactate for energy followed by lactate fermentation. Why does the rate of glycolysis increase significantly when yeast cells switch from aerobic to anaerobic respiration. Why do cancer cells undergo aerobic glycolysis.
Although the immune system normally removes damaged or abnormal cells from the body some cancer cells can hide from the immune system. Others hypothesize that cancer cells develop a defect in mitochondria that leads. This is not always true.
In Ehrlich ascites cells and several other tumors the high aerobic glycolysis is maintained by generation of ADP and P i by the plasma membrane Na K ATPase. Louis Pasteur was one of the first scientists that showed that oxygen can inhibit glycolysis specifically the fermentation process in. The anaerobic process is called glycolysis.
Cancer is defined by uncontrollable cell growth and division so cancer cells need the building blocks and energy to make new cells much faster than healthy cells do. The theoretical evolutionary game theory supports the idea that cells with a higher rate but lower yield of ATP production may gain a selective advantage when competing for shared and limited energy resources xii xiii. MCF-7 breast cancer cells have much lower aerobic glucose consumption rates compared with the highly invasive MDA-mb-231 breast cancer cell line FIG3.
Do cancer cells need energy. 18 Cancer cells exhibit aerobic glycolysis. The high ATPase activity is caused by a defective pump that operates at a low efficiency.
Cancer cells make up 56-63 percent of their ATP budget from aerobic glycolysis. Therefore they rely heavily on the glucose and rapidly convert it to pyruvate via glycolysis. Theoretical calculations using evolutionary game theory support that cells with a higher rate but lower yield of ATP production may gain a selective advantage when competing for shared and limited energy.

Warburg Effect In Cancer Cells In Normal Cells Aerobic Glycolysis Download Scientific Diagram

Schematic Diagram Of Aerobic Glycolysis In Cancer Cell Compared With Download Scientific Diagram

Aerobic Glycolysis Blog De Jose Felix Rodriguez Anton
The Hallmarks Of Cancer 9 Reprogramming Energy Metabolism Jargon Wall

Cellular Atp Provision Defines The Rate Of Aerobic Glycolysis Download Scientific Diagram

Schematics Of Oxidative Phosphorylation Anaerobic Glycolysis And Download Scientific Diagram

The Warburg Effect How Does It Benefit Cancer Cells Abstract Europe Pmc

Warburg Effects A Pkm2 Dimer Mediates Aerobic Glycolysis To Produce Download Scientific Diagram

Schematics Of Oxidative Phosphorylation Anaerobic Glycolysis And Download Scientific Diagram
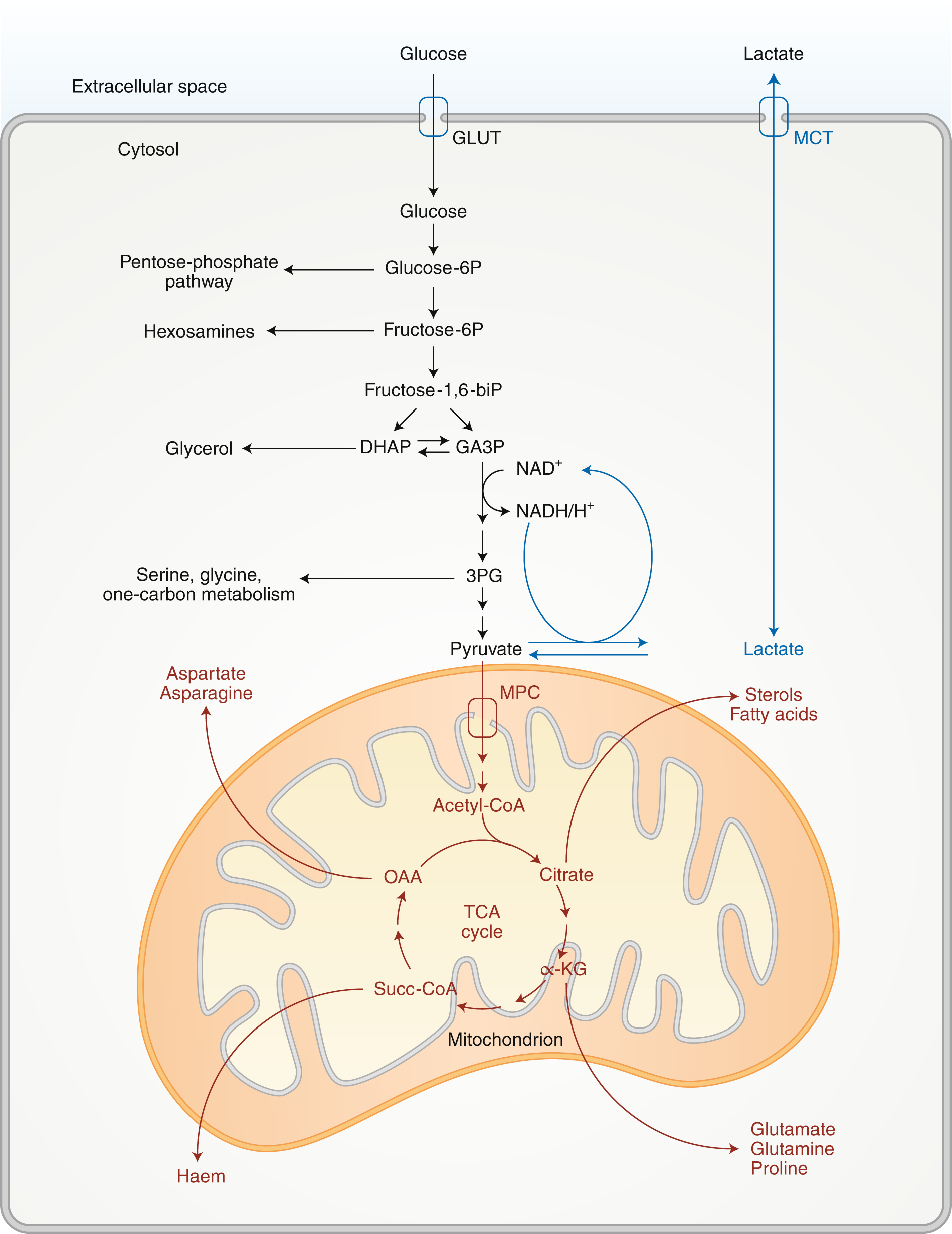
We Need To Talk About The Warburg Effect Nature Metabolism

Function And Regulation Of Glycolysis In Cancer Cells Major Pathways Download Scientific Diagram

Aerobic Glycolysis The Citric Acid Cycle And Key Glycolytic Shunts Download Scientific Diagram

Pi3k Controls The Metabolic Switch To Aerobic Glycolysis In Thymocytes Download Scientific Diagram
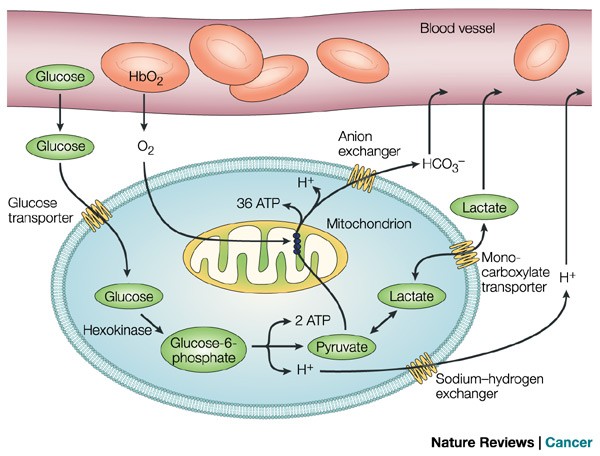
Why Do Cancers Have High Aerobic Glycolysis Nature Reviews Cancer

The Reverse Warburg Effect Aerobic Glycolysis In Cancer Associated Download Scientific Diagram
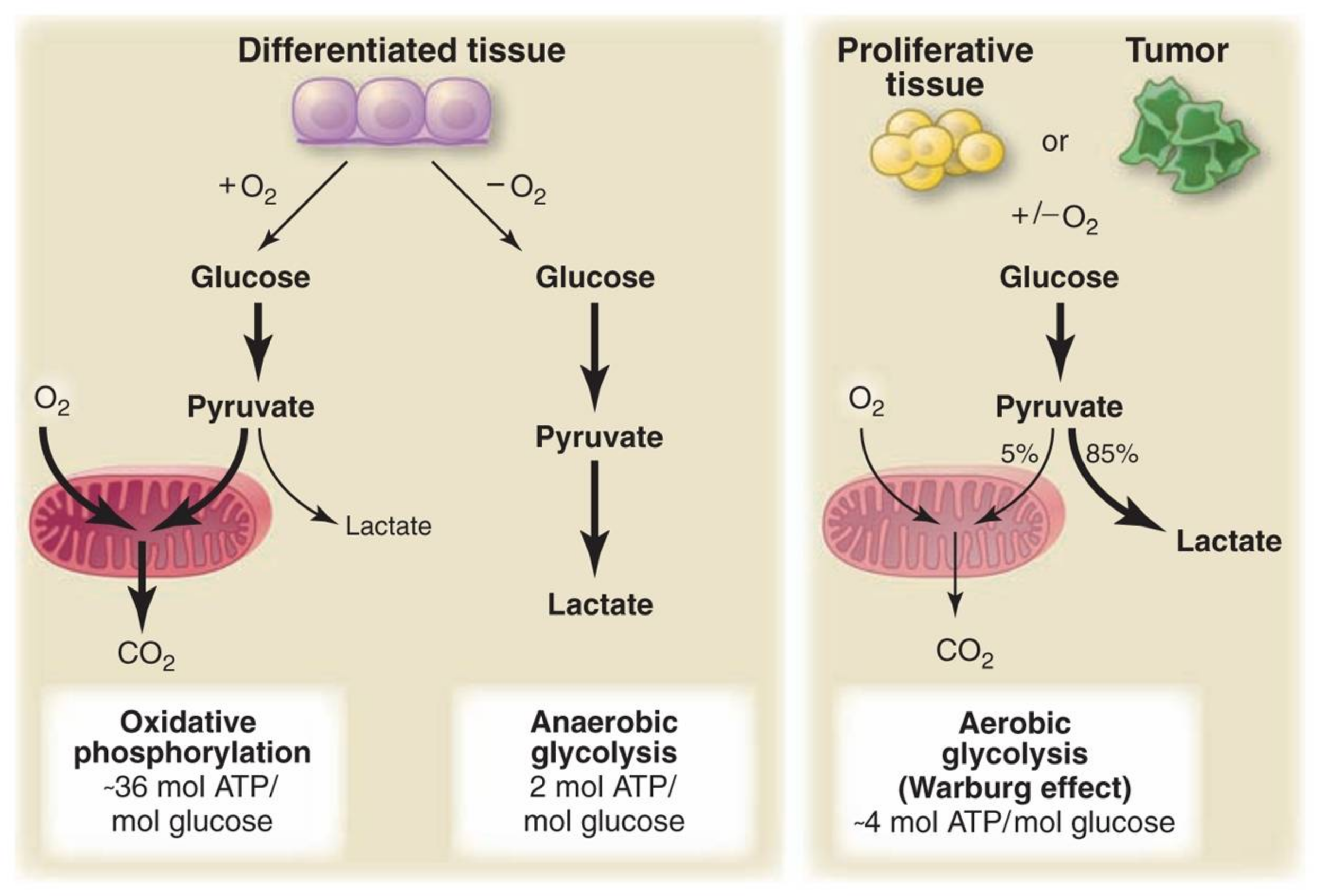
Crossfit Understanding The Warburg Effect The Metabolic Requirements Of Cell Proliferation

Cancers Free Full Text Tumor Energy Metabolism And Potential Of 3 Bromopyruvate As An Inhibitor Of Aerobic Glycolysis Implications In Tumor Treatment Html

Warburg Phenotype Enhanced Aerobic Glycolysis In Cancer Cells Showing Download Scientific Diagram
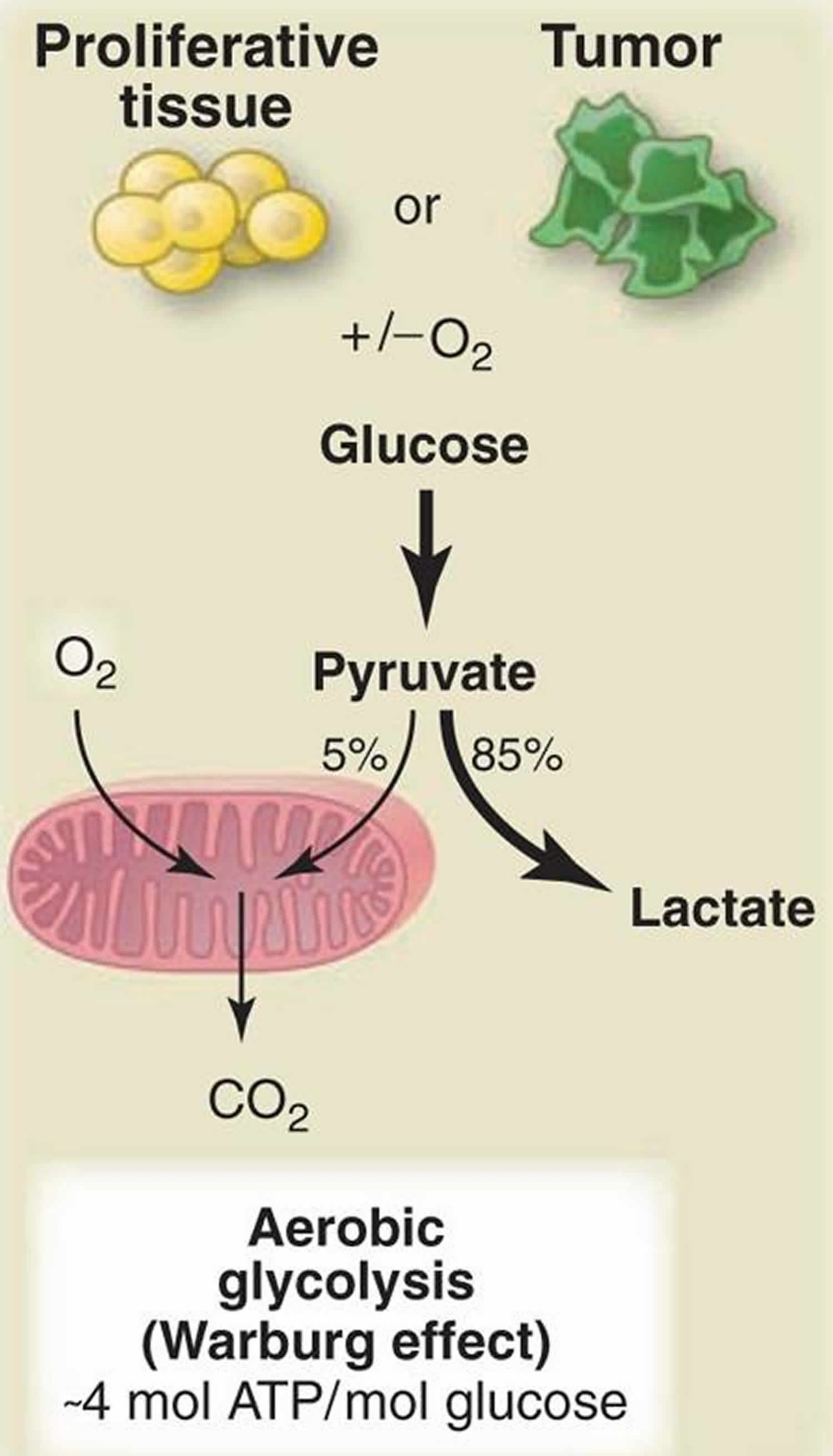
Post a Comment for "KABOOM! Why Do Cancer Cells Use Aerobic Glycolysis"